Introduction
Human resources are one of the essential fsupports of the healthcare system. The performance and benefits that this system can deliver depend largely upon the knowledge, skills, and motivation of those responsible for delivering health services.
The quality of education that MRs, as the future healthcare workforce, receive is threatened worldwide by different forms of abuse, including verbal, physical, sexual, and academic harassment (Chávez-Rivera, Ramos-Lira, & Abreu-Hernández, 2016; Fnais et al., 2013; Fnais et al., 2014; Kulaylat et al., 2017; Li et al., 2010; Nagata-Kobayashi, Maeno, Yoshizu, & Shimbo, 2009; Castro, 2014; Lawrence et al., 2018; Mulder, Ter Braak, Chen, & Ten Cate, 2019). These forms of violence against MRs cannot be evaluated in the same way as that of other workers because the culture of medicine is one of “professional dominance” in which systems and individuals are rarely subject to inquiry. Trainees experiencing humiliation and criticism often think that these are part of normal training (Coverdale, Balon, & Roberts, 2009). In addition, hospitals have a particular hierarchical culture of healthcare that affects the attitudes, values, and behaviours of medical trainees (Ogunsemi, Alebiosu, & Shorunmu, 2010). As well as hierarchical, medical society is androcentric, reproducing within its structure forms of perception, thought, and action tending to keep women and men (who do not meet the social standards of masculinity) in an undervalued space of inability (Jewkes et al., 2015). Gender interaction patterns and GV during medical specialty training may play a decisive role in the ability to perform as professionals (Camargo, Liu, & Yousem, 2017; Crebbin, Campbell, Hillis, & Watters, 2015; Fargen, Drolet, & Philibert, 2016; Kristoffersson, Andersson, Bengs, & Hamberg, 2016; Venkatesh et al., 2016). This also includes worse interactions with patients because they function as a reproduction of the same gender structures that gave rise to it (Castro, 2014).
Previous studies analysed medical students (Wilkinson, Gill, Fitzjohn, Palmer, & Mulder, 2006; Maida et al., 2003) or MRs, but they used questionnaires with three or four items referring to GV (Cohen & Patten, 2005; Montes-Villaseñor, García-González, Blázquez-Morales, Cruz-Juárez, & De-San-Jorge-Cárdenas, 2018; Ortiz-León et al., 2014; Sepúlveda-Vildósola, Mota-Nova, Fajardo-Dolci, & Reyes-Lagunes, 2017; Iglesias-Benavides, Saldívar-Rodríguez, Bermúdez-Barba, & Guzmán-López, 2005; Nagata-Kobayashi et al., 2009). These instruments are useful in the study of outright discrimination and violence; nevertheless, they are insufficient to identify certain kinds of violence characterised by being subdued, with clever forms of control, and with subtle or insidious repetitive and almost invisible behaviours. These poorly perceived behaviours occurred repeatedly during their training and had an important influence on the learning and future performance of medical specialists. Due to their subtlety, they can be replicated across generations if there is no adequate prevention, detection, and intervention. It is important to develop an instrument that helps to identify this kind of violence, because if medical residents do not recognise incidents of GV, they probably will not report them; as in many low-income countries, there is no specific incidence reporting system of GV.
The aim of the present study was to design and analyse the psychometric proprieties of a specific scale that assesses subtle gender-based violence among MRs.
Method
The ethics and scientific committees of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México approved the study procedures. All of the participants took part voluntarily and provided a written informed consent after they received a comprehensive explanation of the study’s nature and procedures.
Design of the study
This study was psychometric, cross-sectional, and analytical, and was conducted among MRs of the UNAM in Mexico City.
Participants
Design phase of the instrument (qualitative phase focal groups)
MRs were invited to participate in focal groups via email (sent by D.GS., G.H., and L.M). A non-probabilistic sampling, using the intensity approach of all cases required for theoretical saturation, was employed, deliberately seeking variation and richness of data by selecting MRs with the characteristics under study (inclusion criteria: Mexican MR of the UNAM, aged 26-40 years, in the first to the fourth years of medical residency), and who, through their communication, were contributing relevant information about GV among MR. The inclusion of new participants was finished when no additional theoretical information was obtained. Participants were recruited from March 2017 to July 2017.
Instrument testing (validation phase)
During an annual meeting, MRs with the same aforementioned inclusion criteria were invited personally by the first author to participate. Given the rule of 10 subjects per item to determine the construct validity via factor analysis, a minimal sample of 620 MRs was required. Participants were recruited from September 2017 to February 2018.
Procedure
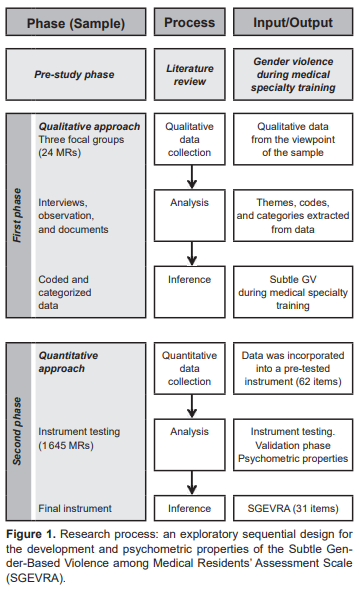
The instrument design was based on the mixed method of sequential exploratory design that consisted of two phases (Creswell & Plano Clark, 2011; Galeano-Marín, 2004) (Figure 1).
(1) Qualitative phase: three focal groups (each one with eight MR) were interviewed twice with a one month interval between the interviews (to facilitate deeper insights and reflection) (Buss-Thofehrn et al., 2013), with a focal group guide (that was built specifically for this study) prepared according to an author’s critical literature review (D.GS., I.VH., A.SA., and D.HM) about GV during medical specialty training (Crebbin et al., 2015; Espinar-Ruiz & Mateo-Pérez, 2007; Fnais et al., 2014; Witte, Stratton, & Nora, 2006) and was used as a support tool to assist the exploration of key issues with MRs.
A total of 24 MRs participated: 50% men (from clinical and surgical specialties courses), with an average age of 29.5 (SD = 2.43, range = 26-34), mostly single (62.5%, n = 15) and without children (75%, n = 18). The interview was conducted by two research psychiatrists with extensive experience in focus groups (I.VH. and D.GS). The audio-recorded information was transcribed and organised for analysis. An inductive thematic analysis was performed. The contents of the interviews were coded, condensed, and categorised (D.GS. and D.HM separately explored and coded the text) with reference to the research objective (Leech & Onwuegbuzie, 2008). Subsequently, the data were organised in mutually exclusive categories based on the a priori established categories of the focal group guide.
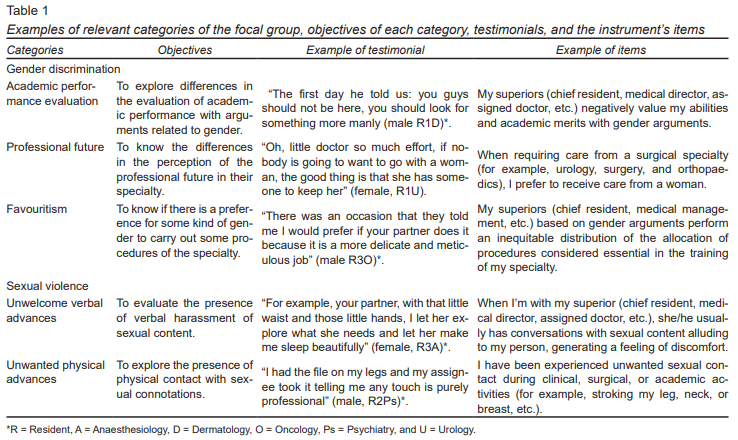
(2) Quantitative phase: the information was incorporated into a 62-item instrument (D.GS., A.FO., and I.VH): a) 55 items were rated on a 5-point Likert agreement scale (from “totally disagree” to “totally agree”); b) seven items were rated on a good/bad Likert scale (Vagias, 2006) (from very good to very bad). Table 1 provides some examples of the items in the categories.
To test the content validity (Yaghmaie, 2003), four gender and sexuality experts (J.RR., A.SG., M.GL, and A.SA), with at least three years’ experience in the field, were asked to rate on a four-point scale each item based on relevance, clarity, simplicity, and ambiguity. Items with a Content Validity Index (CVI) (Waltz & Bausell, 1981) over .80 were retained (mean = .89, SD = .11). Two items were discarded as the experts considered they evaluated discrimination based on sexual orientation. Corrections of style were made in the writing of items with inclusive language, thus integrating a final 60-item instrument divided into two dimensions: gender discrimination (GD) (31 items) and sexual violence (SV) (29 items). The responses were transformed into quantitative variables on a scale of 1 to 5 (1 = strongly disagree, very good; 5 = totally agree, very bad). Subscale scores were calculated as follows: GD was the result of the sum of the scores in each of the items with the Likert agreement scale (31 items) and SV was the sum of the scores of each of the 29 items.
Instrument testing
A pilot study of the instrument was conducted on 1 900 MRs of the UNAM, of which 1 645 physicians (from clinical and surgical specialisation courses) answered the complete instrument, representing an 86% response rate. Overall, 56% (n = 921) were women, with an average age of 30.6 years (SD = 2.94, range = 25-39). Most of the participants were single at the time of the study (96.4%, n = 1586), without children (97.8%, n = 1610), and attending the first two years of their medical specialty (first year = 37.2%, n = 612; second year = 38.7%, n = 636). The average response time was 17.5 (SD = 2.3) minutes.
Statistical analysis
The procedure for testing the construct validity and internal consistency of the instrument was as follows (Rodríguez-Pérez, Valencia-Flores, Reyes-Lagunes, & Lara-Muñoz, 2013): (1) the frequency analysis test and item discrimination index for each item was performed. Items with a single response on more than 90% of the cases were eliminated as well as those with moderate discrimination indexes (< .30). (2) An item total correlation was obtained. Items with moderate indexes (< .20) were eliminated. As a second procedure, we determined the construct validity of the SGEVRA with an exploratory factor analysis with varimax rotation; the suitability of the data for structure detection was indicated by the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin and Bartlett tests. Cattell’s Scree Plot was also obtained. Items with communalities greater than .70 were retained and allocated to factors (Hair, Black, Babin, & Anderson, 2010). Reliability was obtained by determining the internal consistency of the SGEVRA through Cronbach’s alpha. All statistical analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 21. Statistical significance for all analyses was set at an alpha level of < .05 (two-tailed).
Results
Item frequency and discrimination indices
Seven items of the original 60 proposed were eliminated as more than 90% of the participants answered one single response for the items. From the remaining 53, the item discrimination indices ranged from good to excellent with values between .34 to .86. These items were included in the subsequent factor analysis.
Psychometric properties of the SGEVRA
The results of the varimax rotation of the instrument’s 53 items accounted for 71.2% of the variance. The rotated factor matrix exhibited four factors. Factors 3 and 4 consisted of a single item and therefore both were eliminated.
Of the remaining 51 items, 15 showed communalities lower than .70 and were also eliminated. The rationality of those communalities may be that 11 of the items were raised in a reverse grammatical sense. Finally, five additional items were eliminated as they loaded into a theoretical construct different from the one for which they were originally designed.
After these modifications, a second factor analysis was performed. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin sampling adequacy was .87 and a significant Bartlett test (< .001) was obtained. The analysis showed two clear factors that corresponded to the original two designed domains that accounted for 74.98% of the variance. The first factor (58.78% of the variance) contained 21 statements with factor loadings above .83. The second factor (16.21% of the variance) involved 10 statements that loaded at the .70 level or above (Table 2).
The reliability of the SGEVRA obtained by assessing the internal consistency was high. Cronbach’s alpha for the 21-item factor 1 (GD) was .98, and for the 10-item factor 2 (SV) was .93.
Discussion and conclusion
The present study presents psychometric evidence of the validity and reliability of the SGEVRA. The exploratory factor analysis corroborated the adequacy of the two-factor model with good fit indexes for all of the items, whose sum was used as a global measure of the phenomenon. The reliability analysis showed high values of internal consistency.
At the beginning of the focal group, many participants (both sexes) stated that gender did not matter, but they later described numerous subtle experiences of constraining gendered preconceptions and discriminatory treatment. Why did the MRs have difficulties recognising GV during their training? One explanation might be the widespread, everyday communication of gender beliefs combined with the MRs’ normalisation of sexism and gender discrimination. Studies showed that medical residents often do not report an incident of abuse because they are unaware of what qualifies as abuse (Al-Shafaee et al., 2013; Nagata-Kobayashi et al., 2009). They rationalise intimidation and harassment as being a “functional educational tool” (Musselman, MacRae, Reznick, & Lingard, 2005) or they lack knowledge on how and to whom they should report incidents (Al-Shafaee et al., 2013; Coverdale et al., 2009; Nagata-Kobayashi et al., 2009). Studies analysing medical residents’ knowledge of the reporting process showed that only approximately one-half knew the process required to report such mistreatment (Crutcher, Szafran, Woloschuk, Chatur, & Hansen, 2011; Cohen & Patten, 2005). Additionally, some authorities (heads of teaching and academic directors) contemplate these acts as being irrelevant or “normal” (Castro, 2014). The aforementioned constitutes an important finding during the construction of the instrument. However, it could also be considered that one of the benefits of the instrument is the fact that through the reading of items with specific examples of this subtle type of GV, MRs may notice behaviours that would go unnoticed if not directly asked.
The gender experts discarded two items: (1) “your superiors treat you badly because of your sexual orientation” and (2) “you have received offensive jokes related to your sexual orientation by your superiors or colleagues.” Those items were created to assess unwanted attempts to draw MRs into a discussion of sexual matters as a part of sexual violence (Fitzgerald, Gelfand, & Drasgow, 1995), but the group of experts said that those items were evaluating violence based on sexual orientation, which is a type of violence often referred to as homophobic and transphobic violence.
Subsequently, seven items were eliminated, as more than 90% of the participants answered one single response for them: (1) “All people, without distinction of gender, can develop the same activities within a hospital,” (2) “In order not to appear sexist, many men are inclined to overprotect women and overload men with work,” (3) “In my day to day, I apply my beliefs about gender equity,” (4) “I consider that the differences in opportunities due to gender are justified,” (5) “I think there are medical specialties that are more suitable for people of a specific gender,” (6) “I consider status differences between people of different genders are justified by biological reasons,” and (7) “I think in managerial positions, where political and diplomatic skills are required in addition to academic ones, men are better leaders than women.” The almost exclusive answer to these items may be related to the interpretation of them as factual (Haladyna & Rodríguez, 2013) and some may have triggered social desirability concerns (Kreuter, Presser, & Tourangeau, 2008; Tourangeau & Yan, 2007). In other words, MRs underreport undesirable opinions because there are social norms governing some beliefs and/or attitudes so that the participants may misrepresent themselves to appear to comply with these norms (Kreuter et al., 2008). This should be taken into consideration in future studies.
Additionally, 22 items were eliminated: (1) two because the first rotated factor matrix exhibited four factors (two consisted of a single item): “Although before there was discrimination based on gender, at present there are no differences in treatment for this reason.” This may load in a different factor because it evaluated the general opinion of the MRs on GD but did not address specific attitudes (such as the rest of the items in the factor). The second item was: “Some family members of patients negatively value your abilities, effort, work proposals, or attitudes with gender arguments.” This item probably loads in a different factor as the sentence refers to a relative of a patient and not a member of the healthcare staff (other resident doctors, chief residents, and nurses), making it difficult to understand the meaning of the question. Another possibility is that the medical residents thought that the question evaluated a different construct such as public recognition of their medical work. (2) A total of 15 items were redundant and showed communalities lower than 0.70, so they were also discarded (Hair et al., 2010). (3) The remaining five items were eliminated as they loaded into a theoretical construct different from the one for which they were originally designed. The following two questions: “Have you noticed that your superiors tend to look at you with sexual intentions and that makes you feel bad?” and “Have you received comments from your superiors about rewards or academic incentives in exchange for sexual favours?” were designed as part of SV, but probably loaded in a different factor as some of the medical residents considered them a form of GD. The following questions were designed as part of the GD factor but were loaded in the SV factor: “In your work area, men discriminate more for gender reasons” is perhaps an example of confusion between the concept of GV and SV. “How would you rate in ascending order the performance of women in medical-clinical areas (for example, internal medicine)” and “How would you rate in ascending order the performance of men in surgical areas” are perhaps examples of confusion in the change in the response scale (Haladyna & Rodríguez, 2013).
Some limitations should be considered. (1) The SGEVRA does not have a scale to evaluate the frequency of SV and/or GD. (2) It does not include the specific context of a gay MR being harassed by a gay or non-gay MR. (3) It does not include items about GV’s impact on quality of work. (4) As a self-reported instrument, it relies on the honesty of the participants; factors such as: reporting on either powerful people, people with whom they compete professionally, or people they are bound to serve; fear of negative implications and trauma can interfere with the responses. This study had several strengths, such as enrolling over 1 669 participants (24 for the focus groups and 1 645 for the instrument testing). Items for the instrument were generated from an in-depth literature review and focal group interview with the participation of residents of both sexes as well as surgical, clinical, and diagnostic specialties, which allowed the MRs to express their views, attitudes, beliefs, and experiences about both phenomena, and the latter was reviewed by a panel of gender experts. These steps allowed the development of an instrument based on both views (MRs and gender-sexual experts). Further studies should use a confirmatory factor analysis to evaluate the distribution of the items and the adequacy of the two proposed dimensions of the SGEVRA. Also, a cross-cultural validation should be performed including cultural factors that may influence the perception or reporting of the phenomenon.
The consequences of GV often leave indelible scars on the victims and cause strong deterioration in mental health: anxiety, depression, panic attacks, sleep disorders, headaches, cognitive disorders related to attention and memory, feelings of vulnerability, and difficulties in establishing relationships, among others, negatively impact work performance.
It is necessary to provide MRs, teachers, and supervisors with theoretical concepts and knowledge to help them recognise subtle GV, because if they do not recognise incidents of GV, they probably will not report them. Therefore, the SGEVRA as a self-rated questionnaire is a very attractive solution for screening purposes.
SGEVRA is a valid and reliable instrument for measuring a frequent phenomenon that may have important personal and professional implications in this population (subtle GV during medical residency). It is important not to forget that any form of abuse is a serious threat to an environment that allows them to professionally flourish and maintain the highest quality healthcare system possible. Teaching hospitals and medical schools should not forget that in order to guarantee quality medical care, they must guarantee MRs’ physical and mental health.
Funding
Dr. Diana Guízar-Sánchez received a grant from the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) as a doctoral student in health sciences at the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare they have no conflict of interests.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the study participants who provided their time for this research and the following colleagues for their valuable contributions and comments: Jesús Abrahán Ruiz Rosas, MD; Arturo Sandoval Guerra, PSM; Mario Fausto Gómez Lamont, MSc; Francisco Romo-Nava, PhD; and Lugowski-Rivero Czeslaw Kristofer, MEng.